Even the giants, like Intel, are not left alone immune to such hiccups in this fast-spinning technological world. More importantly, the problems faced by the 13th and 14th generations of Intel processors have been especially problematic and have caused so much fuss for both the company and the users. Problems with the said CPUs range from higher operating voltages to constant crashes, definitely marring Intel’s quality control and future prospects. We will break out all the details on which problems are occurring, with which models, and what Intel is doing to fix them in this article.
The core of the problem is an increased operating voltage
High operating voltages are associated with some of the most common issues in Intel’s 13th and 14th generation processors. As such, instability is a popular complaint, with this chip behaving either in crashing too often or with hung systems. Intel has indicated this is the result of a microcode algorithm error that has falsely requested higher voltages and has, therefore, caused the instability (PetaPixel) (Tom’s Hardware).
Models Affected
It does not reside within one model; instead, it covers several of the key processors in their 13th and 14th generations. In detail, these are:
These are among many models in which users have complained of them, with many of them crashing during high-intensity tasks like gaming or video rendering.
Intel’s Response
Intel has already admitted to the problem and has said a microcode patch to address the elevated voltage requests is in development. The firm appealed for those affected by the instability to reach out to Intel Customer Support for help.
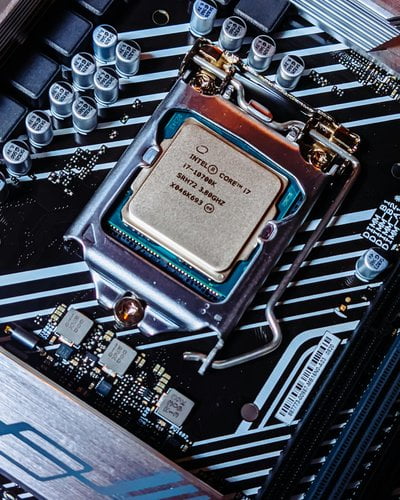

Ripple Effect: Intel Reputation Impact
The instability issues made the end-users very angry and cost Intel its prestige. It covered the whole tech press and influencers, adding to the bad aura. The most reported problems were the abnormally high numbers of crashes with several applications, mainly games using the Unreal Engine.
Stopgap Solutions
Due to these issues, several stopgap solutions were used by Intel and motherboard manufacturers. Those comprised:
- Power Profile Adjustments: Board makers have released new power profiles for Intel processors, which depress power limits often at the expense of some performance.
- BIOS Firmware Updates: Intel directed motherboard manufacturers to halt shipment of all custom BIOS firmware and revert back to their original defaults.
None of the measures resolved the problem, and all are waiting for a permanent fix.
A Tale of Two Generations: 13th vs. 14th
While both the 13th and 14th generations had their own set of problems, there are some minute differences between them.
14th Generation (Raptor Lake Refresh)
The 14th generation, or Raptor Lake Refresh, was supposed to iron out the kinks of its predecessor. Sad to say, many of those problems carried over. Intel’s efforts to deal with that instability via updates and changes to power profiles have only met mixed results. For example, readers who managed to procure an i9- 14900K and i7-14700K noted similar issues to those observed in the 13th generation line.
14th Generation (Raptor Lake Refresh)
The 14th generation, or Raptor Lake Refresh, was intended to iron out the kinks of its predecessor. Unfortunately, it inherited many of the same issues. Intel’s efforts to address the instability with firmware updates and power profile adjustments have been only partially successful. Users of the i9-14900K and i7-14700K have reported similar problems to those seen in the 13th generation.
The Competition: AMD’s Ryzen Advantage
While Intel grapples with these issues, AMD has been milking out of this scenario in every possible way. Their soon-to-be-released Ryzen 9000 series based on Zen 5 cores is the worst possible timing for Intel. AMD chips have significantly impressive reviews over their stability and performance, so have become a go-to alternative for people who get peeved with Intel’s instability issues.
What Does the Future Hold for Intel?
Through all of these, Intel has somehow, to this date, remained the colossal player in the CPU market. The company is tirelessly working on patching the reported issues with their 13th- and 14th-generation processors. While a microcode patch is expected as early as mid-August, it will finally fix the elevated voltage problem.
The Future: Intel Core Ultra 200 (Arrow Lake)
Coming up next for Intel, on the other side of the horizon, is the Core Ultra 200 series—projected as Arrow Lake. Power performance and efficiency are what to expect with this next generation. Yet, problems related to instability in the 13th and 14th generations generate doubt about the upcoming launch. Intel will have to exercise a lot of care to ensure that Arrow Lake doesn’t fall into the same traps as its predecessors.
Conclusion
Instability issues with the 13th and 14th generation processors are a major setback for Intel. Users have expressed their frustration over the high operating voltage, as well as the frequent crashes these have had, which have affected the goodwill of the brand. At the same time, stopgap solutions have certainly been welcome, but there has, thus far, been a pending demand for a permanent fix. Now that Intel is going to bring its next generation of processors into the market, learning from these mistakes and restoring confidence among consumers will be extremely important.
Pain points they are very vocal and clear about; at least an upcoming microcode patch is a step in the right direction. The whole tech world will have eyes on how Intel bucks up to face these challenges and what new springs forth for its processors.















One thought on “Intel Still Has Problems with Processor Models of the 13th and 14th Generations”